Table of Contents
Perceptual map is a strategic compass, a research tool that guides businesses into making well-informed decisions. It is the one that provides insights into the thought process of a target audience or a consumer about their sincere viewpoints about a brand’s product or service. While the concept of perceptual mapping may seem straightforward, executing it is both an art and a science.
Whether your brand is a market leader or a follower, understanding your customers is essential for your growth. This article will delve deep into the concept of perceptual mapping, exploring how it shapes branding, its advantages and disadvantages, and how to use it.
READ ALSO: Online Advertising for Small Business (2023)
What is a Perceptual Map?
Also known as a position map or brand map, it is a visual representation of how a brand’s target audience perceives and positions the products, services, and brand in relation to another brand within the same industry. This map helps to analyse the ideal customer’s perspective, needs, and preferences.
The concept of perceptual mapping can be categorised into two:
- Individual: This is the type of mapping that involves only one brand. The attributes that are most significant in such a brand is the factor considered. Such mapping will be conducted based on how customers view the brand in relation to the already identified attributes.
- Comparative: Just like the name implies, this type of mapping requires the comparison of two brands. The original brand that is yours and a competitor’s within the same niche. This mapping demands that one gather data on the two brands and create a map to illustrate the relative positions of these brands based on chosen attributes. This gives insights into the differences and similarities between the two brands.
The selection of products or brands depends on the specific goals and objectives of the mapping and the level of interest in either analysing your brand in isolation or in comparison to others in the market.
Proven Advantages of Perceptual Maps
When it comes to understanding consumer perceptions about the product or service they offer and making wise decisions, this map offers numerous benefits to marketers and brand owners. They include:
- Customer Insight: It aids in uncovering hidden customer insight. It exposes unpredictable viewpoints that can influence a brand’s marketing strategies and communication tactics. For example, a jewellery business might discover in its perceptual mapping that customers associate its product with bespoke elegance. The marketing strategy can then concentrate on the brand’s commitment to providing customers with custom-made pieces.
- Product Development: A perceptual map guides a business in its developmental efforts. Since it provides sincere feedback on a brand’s product or service, it will equip such businesses with knowledge of what to adjust, work on, and improve.
- Identify current position: Businesses can use perceptual maps to identify their current position in the market and determine their desired position.
- Competitive analysis: By analysing the map, businesses understand the competitive landscape. They can identify areas where a customer’s demand was not met or competitors are weak, providing opportunities for innovation and expansion.
- Segmentation: A perceptual map helps with market segregation. As it identifies groups of consumers with similar perceptions, brands can incorporate efforts to suit each category of target audience views
READ ALSO: Competitive Analysis for Entrepreneurs: A Detailed Guide (2023)
A Typical Example of a Perceptual Map
Let us consider a hypothetical perceptual map for a domestic shopping platform where two dimensions are used to position a domestic African Store. This store might map its perception along the lines of “high priced” and “high authenticity” and its opposites relative to its other products.
This example will use a two-dimensional map to illustrate the African store. However, a perceptual map can be complex with many dimensions.
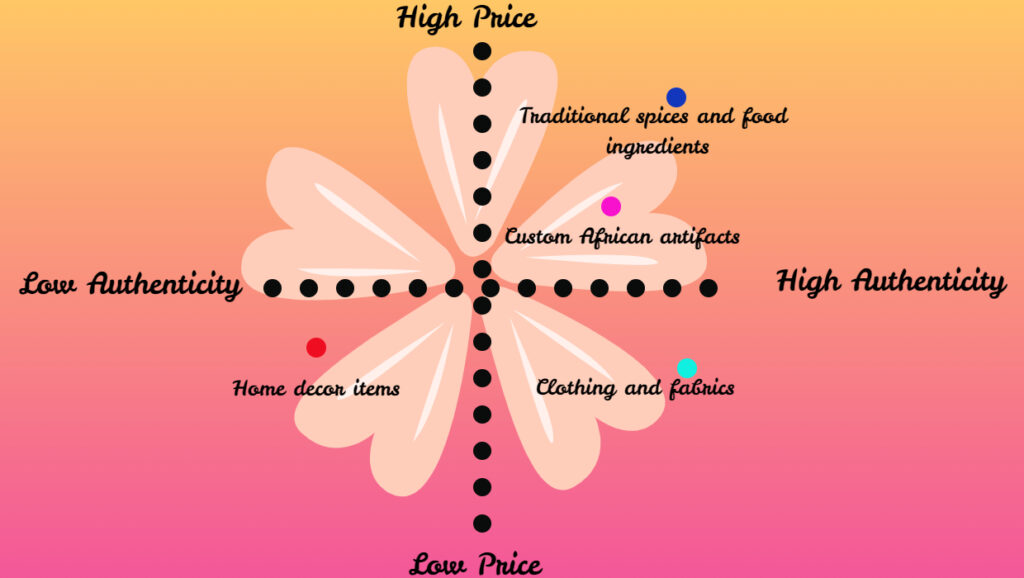
The products are positioned according to their perceived authenticity (X-axis) and their price range (Y-axis) High authenticity is on the right side of the map, while low authenticity is at the lower part of the map. The low price range is at the bottom, while the high price range is at the top.
5 Limitations of Perceptual Maps

Various limitations often influence the results of a perceptual map. Despite these limitations, a map is a useful tool for learning about customer opinions. They offer ideas for strategic decision-making when used in conjunction with additional research methods.
- Streamlines Reality: Perceptual maps are simplified representations of target audience preferences. They condense these preferences into two or three dimensions, which may not capture the range of factors that influence consumer behaviour and choices.
- Discrepancies in Data Collection: Gathering accurate and generalisable data for a perceptual map can be challenging; some respondents may not be sincere in their responses, and other data collection methods may not elicit an honest response from customers. Inaccuracies in data collection can skew the results.
- Interpretation: Analysing and interpreting a perceptual map can be challenging because some maps are complex, especially with multiple dimensions.
- Dynamic Nature: A perceptual map is needed at intervals. This is because the perceptions of customers change from time to time, so, it becomes a problem when it is outdated and needs to be updated.
- Influence of External Factors: The perception of customers can be informed by different factors outside the dimensions on the map, such as social trends or economic conditions.
What Prework Should be Done Before a Perpetual Map Session?
It is important to note that a perceptual mapping analysis involves a systematic process. As a result, some preliminary actions must be taken before a map session. This forms the premise and ensures one can proceed to an impactful mapping session. The prework steps include the following:
- Definition of Objectives and Goals: No process does not have the backing of the set aims and objectives of the mapping. Decide on what you want to achieve at the end of the process, whether to understand your brand position, competitive gaps, or customer opinions.
- Determination of Attributes: This stage is where the attributes that are most significant in a brand are highlighted. This will prepare the mapping session to find out how customers view the brand in relation to the already identified attributes.
- Collection of Data: To run a pretesting, collect data from a sample of your target audience population about their perspective on the products or brands, as the case may be. The data can be collected via surveys, customer reviews, market research, or any other reliable source.
- Scale of Measurement: Decide on the scale and measurement for attributes. For instance, you could use a five-point scale to assess the quality of a product. That is very low, low, neutral, high, and high.
- Mapping Technique: Select the appropriate tools or software for data analysis. A common method used is multidimensional analysis.
- Map Creation: The next step is to create a perpetual map using the chosen analysis method, plotting the products and services based on their perceived attributes.
READ ALSO: How to Do Market Research for Startups (2023)
6 Steps to Conduct Perceptual Mapping
- Data Analysis: Use the chosen technique to analyze the data. This involves mathematical calculations to determine the positions of items.
- Create the Perceptual Map: Based on the analysis, create a perceptual map. This map uses a two-dimensional graph, X and Y axis, with each axis representing a factor or dimension derived from the analysis. Plot the items (products, attributes) on the map according to their positions.
- Label the Map: Label the map with the names or identifiers of the products or brands so that it’s clear which point on the map corresponds to each item.
- Interpret the Map: Analyze the map to understand the opinions of customers and the relationships and positions of the products and services in the market space.
- Segmentation: Consider using the map to identify market segments or clusters of similar products. This helps in targeting specific customer groups.
- Competitive Analysis: Assess how your products or services compare to competitors on the map. Are there gaps or opportunities for differentiation? Use it to inform marketing strategies, product development, positioning adjustments, or other business decisions.
READ ALSO: How to Use the Right Media Partner to Sell Your Product
How do you Make the Most Out of Perceptual Mapping?
Maximizing the benefits of perceptual mapping involves taking insights from the map to make strategic marketing decisions. Here is a summary of how to do that:
- Understand the map: To start, fully comprehend the perceptual map you developed. Identify the dimensions or items used to create the map, such as the cost, value, and placement of your brand or product in relation to the competition.
- Identify Opportunities: Look for any gaps or underrepresented points on the map. These are prospective market opportunities where you might introduce a new product or service. Additionally, examine the map to see if there are places where customers have similar perceptions. You can segment the market with categories to more effectively target specific customer segments.
- Conduct competitive analysis: Assess the positioning of your competitors on the map. Identify areas where your brand can differentiate itself or where you can compete more effectively. Determine whether your brand’s positioning aligns with your desired image and market strategy. If not, consider repositioning your brand accordingly.
- Product Development: Use the perceptual map to guide product development efforts. Identify areas where consumers seek specific attributes or qualities, and tailor your product offerings to meet these needs.
- Branding: Ensure that your brand’s visual identity aligns with its position on the map. Consistency in branding reinforces customers’ perceptions.
- Continuous Monitoring: Customer’s perceptions can change over time, for this reason, continuously monitor the market and update the perceptual map as needed to stay updated.
- Feedback: Seek feedback from customers and team members to validate the insights from the perceptual map.
READ ALSO: How to Generate Leads for Business Using Advertising (2023)
Conclusion
Through perceptual maps, companies get to identify their position in the market, and the sentiment of their customers about their goods and services, and discover opportunities for growth. Nonetheless, It is important to remember that a perceptual map is a dynamic reflection of the ever-evolving market space.
By leveraging the discoveries of the perceptual map, businesses can adapt to emerging trends, listen to the customer’s needs, and utilise the map to their advantage.
FAQs ABOUT PERCEPTUAL MAPS
How often are perceptual maps updated?
Perceptual map is often updated within the timeframe of 6 to 12 months. However, this update’s frequency is based on several factors, such as the type of industry/niche, specific goals, and product changes.
What is the best medium for perceptual map sessions?
There is no fixed answer, as it depends on various factors. The mediums to use despite that include online collaboration tools like Google Workspace, printed templates, video conferences, software, whiteboards, or flipcharts.
Why are perceptual maps updated?
The maps are updated due to customers’ dynamic and unpredictable opinions, product change, marketing efforts, market entry and expansion, feedback, or to track changes in branding.

